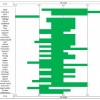
Abstract
Soil pH affects nutrient bioavailability by controlling the chemical forms of nutrients. This 11-page fact sheet provides information about soil pH basics to commercial growers, county Extension agents, and college students specializing in vegetable production. Written by Guodong Liu and Edward Hanlon, and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, October 2012.
HS1207/HS1207: Soil pH Range for Optimum Commercial Vegetable Production (ufl.edu)
References
Costa, A. C. S. d., and E. P. Seidel. 2010. "Nitrate Leaching from a Latosol after Application of Liquid Swine Manures in Different pH Values and Organic Matter Contents." Acta Sci., Agron 32 (4): 743-748. https://doi.org/10.4025/actasciagron.v32i4.10070
Das, A., R. Prasad, A. Srivastava, P. H. Giang, K. Bhatnagar, and A. Varma. 2010. "Fungal Siderophores: Structure, Functions and Regulation." In Microbial Soderophores (Soil Biology), edited by A. Varma and S. B. Chincholkar, 1-42. Heidelberg, Germany: Springer-Verlag. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-71160-5_1
Fageria, N. K., and F. J. P. Zimmermann. 1998. "Influence of pH on Growth and Nutrient Uptake by Crop Species in an Oxisol." Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis 29 (17&18): 2675-2682. http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/00103629809370142. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103629809370142
Finck, A. 1976. Pflanzenernährung in Stichworten. Kiel, Germany: Verlag Ferdinand Hurt.
Havlin, J. L., J. D. Beaton, S. L. Tisdale, and W. L. Nelson. 2005. Soil Fertility and Fertilizers: An Introduction to Nutrient Management. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education.
Kioke, S., K. V. Subbarao, R. M. David, and T. A. Turini. 2003. Vegetable Diseases Caused by Soilborne Pathogens. Publication 8099. Davis: University of California Division of Agriculture and Natural Resources. http://ucanr.org/freepubs/docs/8099.pdf. https://doi.org/10.3733/ucanr.8099
Kissel, D. E., and L. Sonon, eds. 2008. Soil Test Handbook for Georgia. Athens: University of Georgia. Accessed May 11, 2011. http://aesl.ces.uga.edu/publications/soil/STHandbook.pdf.
Lidon, F. C., and M. G. Barreiro. 1998. "Threshold Aluminum Toxicity in Maize." Journal of Plant Nutrition 21 (3): 413-419. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904169809365413
Liu, G. D., J. Dunlop, T. Phung, and Y. C. Li. 2007. "Physiological Responses of Wheat Phosphorus-Efficient and -Inefficient Genotypes in Field and Effects of Mixing Other Nutrients on Mobilization of Insoluble Phosphates in Hydroponics." Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis 38 (15-16): 2239-2256. http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/00103620701549249. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103620701549249
Neumann, G., and V. Romheld. 2012. "Rhizosphere Chemistry in Relation to Plant Nutrition." In Marschnar's Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants (3rd ed.), edited by P. Marschnar, 347-368. New York: Elservier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-384905-2.00014-5
Osakia, M., T. Watanabe, and T. Tadano. 1997. "Beneficial Effect of Aluminum on Growth of Plants Adapted to Low pH Soils." Soil Science and Plant Nutrition 43 (3): 551-563. https://doi.org/10.1080/00380768.1997.10414782
Relley, H. E., and C. L. Shry, Jr. 1997. Introductory Horticulture (5th ed.). Albany, NY: Demar Publishers.
Ronen, E. 2007. "Micro-Elements in Agriculture." Practical Hydroponics & Greenhouses July/August: 39-48.
Sylvia, D. M., J. F. Fuhrmann, P. G. Hartel, and D. A. Zuberer. 2005. Principles and Applications of Soil Microbiology. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education.
Splittstoesser, W. E. 1990. Vegetable Growing Handbook: Organic and Traditional Methods (3rd ed.). New York: Chapman & Hall.
Thomson, C. J., H. Marschner, and V. Römheld. 1993. "Effect of Nitrogen Fertilizer Form on pH of the Bulk Soil and Rhizosphere, and on the Growth, Phosphorus, and Micronutrient Uptake of Bean." Journal of Plant Nutrition 16 (3): 493-506. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904169309364548
USDA (United States Department of Agriculture). 1976. "Soil Survey of Palm Beach County Area, Florida." Natural Resources Conservation Service. Accessed October 16, 2012. http://soildatamart.nrcs.usda.gov/manuscripts/FL611/0/Palm_Beach.pdf.
USDA (United States Department of Agriculture). 1979. "Soil Survey of Jackson County Area, Florida." Natural Resources Conservation Service. Accessed October 16, 2012. http://soildatamart.nrcs.usda.gov/manuscripts/FL063/0/Jackson.pdf.
USDA (United States Department of Agriculture). 1983. "Soil Survey of St. Johns County Area, Florida." Natural Resources Conservation Service. Accessed October 16, 2012. http://soildatamart.nrcs.usda.gov/Manuscripts/FL109/0/StJohns.pdf.
USDA (United States Department of Agriculture). 1993. "Soil Survey Manual: Chapter 3." Natural Resources Conservation Service. Accessed May 22, 2012. http://soils.usda.gov/technical/manual/contents/chapter3.html.
USDA (United States Department of Agriculture). 1996. "Soil Survey of Dade County Area, Florida." Natural Resources Conservation Service. Accessed October 16, 2012. http://soildatamart.nrcs.usda.gov/manuscripts/FL686/0/Dade.pdf.
Wright, A. L., E. A. Hanlon, J. M. McCray. 2009. Fate of Phosphorus in Everglades Agricultural Soils after Fertilizer Application. SL290. Gainesville: University of Florida Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences. http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ss503.