Abstract
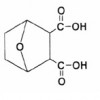
Endothall is the herbicidal active ingredient found in commercial formulations labeled for weed control in aquatic systems and on ditch banks. It is also used as a defoliant and desiccant in some terrestrial situations (e.g., in potato, hops, cotton, clover, and alfalfa production). This 7-page fact sheet introduces users of endothall to the physical, chemical, environmental, and ecological properties of this herbicidal active ingredient relative to the aquatic environment. Written by P. Chris Wilson and Jun Wu, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, October 2012.
References
"Chemical Structure Index - Endothall." 2011. Bugwood. Accessed July 2012. http://www.bugwood.org/PAT/22chemicalstructures.html#Endothall.
Comes, R.D., D.W. Bohmont, and H.P. Alley. 1961. "Movement and Persistence of Endothall (3,6-endoxohexahydrophthalic acid) as Influenced by Soil Texture, Temperature, and Moisture Levels." J. Am. Soc. Sugar Beet Technol. 11:287-93. https://doi.org/10.5274/jsbr.11.4.287
Haller, W.T., and D.L. Sutton. 1973. "Factors Affecting the Uptake of Endothall 14C by Hydrilla." Weed Sci. 21:446-8. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0043174500027466
Hiltibran, R.C. 1962. "Duration of Toxicity of Endothall in Water." Weeds 10:17-19. https://doi.org/10.2307/4040552
Holmberg, D.J., and G.F. Lee. 1976. "Effects and Persistence of Endothall in the Aquatic Environment." Journal (Water Pollution Control Federation) 48:2738-46.
HSDB (Hazardous Substance Data Bank). 2011. U.S. National Library of Medicine. Accessed July 2012. http://toxnet.nlm.nih.gov/cgi-bin/sis/htmlgen?HSDB.
Jenson, H.L. 1964. "Studies on Soil Bacteria (Arthrobacter globiformis) Capable of Decomposing the Herbicide Endothall." Acta. Agr. Scand. 14:193-204. https://doi.org/10.1080/00015126409434166
Keckemet, O., and R.T. Nelson. 1968. "Mode of Action, Persistence and Fate of Endothall in the Aquatic Environment." Proc. South. Weed Sci. Soc. 21:45-6.
Langeland, K.A., and J.P. Warner. 1986. "Persistence of Diquat, Endothall, and Fluridone in Ponds." J. Aquat. Plant Manage. 24:43-6.
MacDonald, G.E., D.G. Shilling, and T.A. Bewick. 1993. "Effects of Endothall and Other Aquatic Herbicides on Chlorophyll Fluorescence, Respiration and Cellular Integrity." J. Aquat. Plant Manage. 31:50-4.
Mann, J.D., and M. Pu. 1968. "Inhibition of Lipid Synthesis by Certain Herbicides." Weed Sci. 16:197-8. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0043174500046890
Montgomery, M.L., and V.H. Freed. 1964. "Metabolism of Endothall." Mimeo Report. Tacoma, WA: Penwalt Chem. Corp.
Reinert K.H., and J.H. Rodgers, Jr. 1984. "Influence of Sediment Types on the Sorption of Endothall." Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 32:557-64. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01607537
Reinert, K.H., M.L. Hinman, and J.H. Rodgers, Jr. 1988. "Fate of Endothall during the Pat Mayse Lake (Texas) Aquatic Plant Management Program." Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 17:195-9. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01056025
Reinert, K.H., J.H. Rodgers, Jr., M.L. Hinman, and T.J. Leslie. 1985. "Compartmentalization and Persistence of Endothall in Experimental Pools." Ecotox. Environ. Safe.10:86-96. https://doi.org/10.1016/0147-6513(85)90010-7
Sikka H.C., and J. Saxena. 1973. "Metabolism of Endothall by Aquatic Microorganisms." J. Agric. Food Chem. 21:402-6. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf60187a034
Sikka, H.C., and C.P. Rice. 1973. "Persistence of Endothall in Aquatic Environment as Determined by Gas-Liquid Chromatography." J. Agr. Food Chem. 21:842-6. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf60189a014
Sikka H.C., D. Ford, and R.S. Lynch. 1975. "Uptake, Distribution, and Metabolism of Endothall in Fish." J. Agric. Food Chem. 23:849-51. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf60201a009
Simsiman, G.V., and G. Chesters. 1975. "Persistence of Endothall in the Aquatic Environment." Water, Air, and Soil Pollution 4:399-413. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00280725
Simsiman, G.V., T.C. Daniel, and G. Chesters. 1976. "Diquat and Endothall: Their Fates in the Environment." Residue Rev. 62:131-74. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4613-9404-4_11
Sprecher, S.L., K.D. Getsinger, and J. Sharp. 2002. Review of USACE-Generated Efficacy and Dissipation Data for the Aquatic Herbicide Formulations Aquathol® and Hydrothol®. Washington, D.C.: U.S. Army Corps of Engineers. https://doi.org/10.21236/ADA403770
Tomlin, C. 2004. The e-Pesticide Manual, 13th ed. Crop Protection Publications, British Crop Protection Council.
Thomas, T.M., and D.E. Seaman. 1968. "Translocation Studies with Endothall-14C in Potamogeton nodosus Poir." Weed Res. 8:321. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3180.1968.tb01436.x
Tsay, R-C., and F.M. Ashton. 1971. "Effect of Several Herbicides on Dipeptidase Activity of Squash Cotyledons." Weed Sci. 19:682-4. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0043174500051055
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (U.S. EPA). 1992. Drinking Water Criteria Document (Final Report). Health and Ecological Criteria Division, Office of Science and Technology, Office of Water. Washington, D.C.: U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.
U.S. EPA. 2005. Agency Reregistration Eligibility Decision for Endothall. EPA 738-R-05-008. Washington, DC: U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.
Vencill, W.K. 2002. Herbicide Handbook, 8th ed. Lawrence, KS: Weed Science Society of America.
Verschueren, K. 2001. Handbook of Environmental Data on Organic Chemicals Volumes 1-2, (4th ed). New York, NY: John Wiley & Sons.
Walker, C.R. 1963. "Endothall Derivatives as Aquatic Herbicides in Fishery Habitats." Weeds 11:226-32. https://doi.org/10.2307/4040590
Wauchope, R.D., T.M. Buttler, A.G. Hornsby, P.W.M. Augustijn-Beckers, and J.P. Burt. 1992. "The SCS/ARS/CES Pesticide Properties Database for Environmental Decision-making." Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 123: 161. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4612-2862-2_1
Weber, J.B. 1994. "Properties and Behavior of Pesticides in Soil." In Mechanisms of Pesticide Movement into Ground Water, edited by Richard C. Honeycutt and Daniel J. Schabacker, 15-41. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781351074346-3
Westerdahl, H.E., and K.D. Getsinger. 1988. Aquatic Plant Identification and Herbicide Use Guide, Volume I: Aquatic Herbicides and Application Equipment. Vicksburg, MS: Environmental Laboratory, Department of the Army.
Wilson, C. 2006. Aquatic Toxicology Notes: Predicting the Fate and Effects of Aquatic and Ditchbank Herbicides. SL236. Gainesville, FL: University of Florida Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences. http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ss455. https://doi.org/10.32473/edis-ss455-2006
Yeo, R.R. 1970. "Dissipation of Endothall and Effects on Aquatic Weeds and Fish." Weed Sci. 18:282-4. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0043174500079765