Abstract
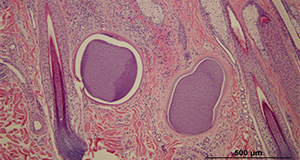
Besnoitiosis is a skin condition affecting donkeys in Florida and throughout the United States. This publication discusses the condition as well as clinical findings, diagnosis, prevention, and therapy. Written by Sally DeNotta, and published by the UF/IFAS Veterinary Medicine—Large Animal Clinical Sciences Department, January 2023.
References
Bennett, S. C. 1927. “A Peculiar Equine Sarcosporidium in the Anglo-Egyptian Sudan.” Vet. J. 83:297–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0372-5545(17)42817-3
Bennett, S. C. 1933. “Globidium Infections in the Sudan.” J. Comp. Path. Thera. 46:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0368-1742(33)80002-6
Davis, W. P., D. F. Peters, and R. W. Dunstan. 1997. “Case Report: Besnoitiosis in a Miniature Donkey.” Vet. Dermatol. 8:139–143. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-3164.1997.d01-1.x
Dubey, J. P., and D. S. Lindsay. 2003. “Development and Ultrastructure of Besnoitia oryctofelisi Tachyzoites, Tissue Cysts, Bradyzoites, Schizonts and Merozoites.” Int. J. Parasitol. 33:807–819. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0020-7519(03)00087-0
Dubey, J. P., C. Sreekumar, T. Donovan, et al. 2005. “Redescription of Besnoitia bennetti (Protozoa: Apicomplexa) from the Donkey (Equus asinus).” Int. J. Parasitol. 35:659–672. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpara.2005.01.004
Dubey, J. P., C. Sreekumar, B. M. Rosenthal, et al. 2004. “Redescription of Besnoitia tarandi (Protozoa: Apicomplexa) from the Reindeer (Rangifer tarandus).” Int. J. Parasitol. 34:1273–1287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpara.2004.07.002
Dubey, J. P., and M. J. Yabsley. 2010. “Besnoitia neotomofelis n. sp. (Protozoa: Apicomplexa) from the Southern Plains Woodrat (Neotoma micropus).” Parasitology 137:1731–1747. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0031182010000636
Elsheikha, H. M., C. D. Mackenzie, B. M. Rosenthal, et al. 2005. “An Outbreak of Besnoitiosis in Miniature Donkeys.” J. Parasitol. 4:877–881. https://doi.org/10.1645/GE-3277.1
Jacquiet, P., E. Liénard, and M. Franc. 2010. “Bovine Besnoitiosis: Epidemiological and Clinical Aspects.” Vet. Parasitol. 174:30–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2010.08.013
Lienard, E., A. Nabuco, S. Vandenabeele, et al. 2018. “First Evidence of Besnoitia bennetti Infection (Protozoa: Apicomplexa) in Donkeys (Equus asinus) in Belgium.” Parasit. Vectors 11(1): 427. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-018-2993-3
Ness, S. L., J. Peters-Kennedy, G. Schares, et al. 2012. “Investigation of an Outbreak of Besnoitiosis in Donkeys in the Northeastern United States.” J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 240(11): 1329–1337. https://doi.org/10.2460/javma.240.11.1329
Ness, S. L., G. Schares, J. Peters-Kennedy, et al. 2014. “Serological Diagnosis of Besnoitia bennetti Infection in Donkeys (Equus asinus).” J. Vet. Diagn. Invest. 26(6): 778–782. https://doi.org/10.1177/1040638714550180
Olias, P., B. Schade, and H. Mehlhorn. 2011. “Molecular Pathology, Taxonomy and Epidemiology of Besnoitia Species (Protozoa: Sarcocystidae).” Infection, Genetics and Evolution 11:1464–1576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meegid.2011.08.006
Schares, G., W. Basso, and M. Majzoub, et al. 2010. “Comparative Evaluation of Immunofluorescent Antibody and New Immunoblot Tests for the Specific Detection of Antibodies against Besnoitia besnoiti Tachyzoites and Bradyzoites in Bovine Sera.” Vet. Parasitol. 171:32–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2010.03.017
Terrell, T. G., and J. L. Stookey. 1973. “Besnoitia bennetti in two Mexican Burros.” Vet. Path. 10:177–184. https://doi.org/10.1177/030098587301000210