Exploration of NPTX2 in Islets of Langerhans
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.32473/ufjur.v21i2.108732Keywords:
type 1 diabetes, NPTX2, pancreasAbstract
NPTX2 (neuronal pentraxin-2) is a synaptic protein found abundantly in only two locations in a healthy human body: the brain and the pancreas, specifically islet of Langerhans cells. NPTX2’s role in the brain has been a focus of study in the pathology of Parkinson’s disease, as it is upregulated in PD patients. Its primary functions in the brain are to establish excitatory synapses and to recruit alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA)-type glutamate receptors to said synapses. These AMPA receptors signal for the neurotransmitter, glutamate, that regulates insulin secretion. This is of pathological significance to the onset of type 1 diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is characterized by the depletion of islet β-cells in the pancreas, which are responsible for insulin secretion. Without a supply of insulin, fatal consequences will ensue.
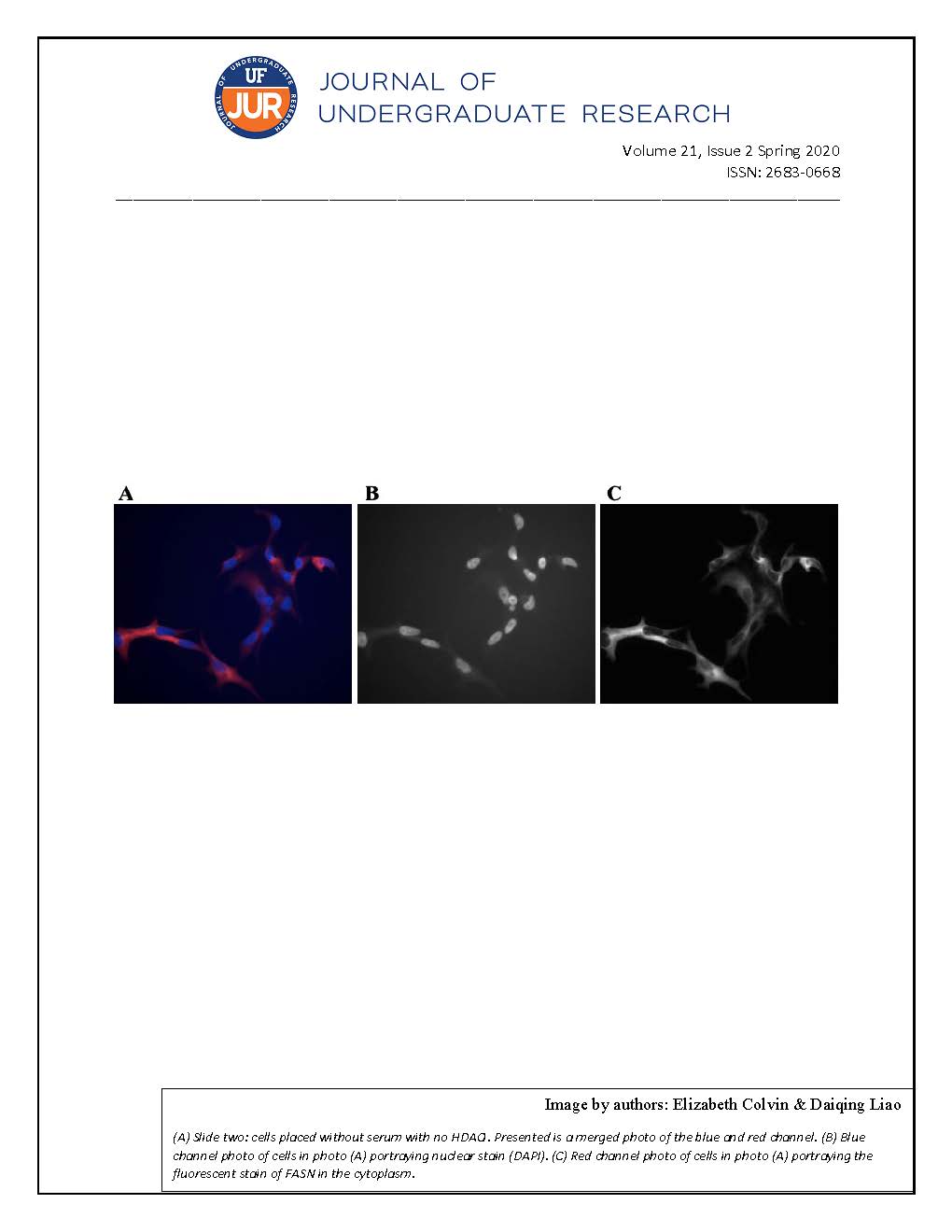
NPTX2’s function in the pancreas is unstudied and extremely relevant to unraveling the complex processes that the body undergoes with the onset of this autoimmune disease. In recent mRNA studies, NPTX2 mRNA was significantly downregulated in type 1 diabetes. To understand the underlying cause of this downregulation and its potential role in the destruction of islet β-cells, it is first necessary to localize NPTX2 in the islet cells of type 1 diabetic, auto-antibody positive, and control donors. Immunofluorescent staining indicates that NPTX2’s co-expression in
References
Atkinson, M.A., Eisenbarth, G.S., Michels, A.W. (2014). Type 1 diabetes. Lancet, 383, 69-82.
Bonifacio, E., (2015). Predicting Type 1 Diabetes Using Biomarkers. Diabetes Care, 38(6), 989-996. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc15-0101
Calderon, B., Sacks, D.B. (2014). Islet Autoantibodies and Type 1 Diabetes: Does the Evidence Support Screening?. Clinical Chemistry, 60(3), 38-440. https://doi.org/10.1373/clinchem.2013.212381
Canzano, J.S., Nasif, L.H., Butterworth, E.A., Fu, D.A, Atkinson, M.A., Campbell-Thompson, M.(2018). Islet Microvasculature Alterations with Loss of Beta-cells in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes. J Histochemistry and Cytochemistry, 67(1), 41-52. https://doi.org/10.1369/0022155418778546
JDRF nPOD Online Pathology Information. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://www.jdrfnpod.org/for-investigators/online-pathology-information/
O'Brien, R.J., Xu, D., Petralia, R.S., Steward, O., Huganir, R.L., Worley, P. (1999). Synaptic clustering of AMPA receptors by the extracellular immediate-early gene product Narp. Neuron,23(2), 309-323.
Omeis, I.A., Hsu, Y.C., Perin, M.S. (1995). Mouse and human neuronal pentraxin 1 (NPTX1):conservation, genomic structure, and chromosomal localization. Genomics, 28(2), 220. https://doi.org/10.1006/geno.1996.0503
Tissue expression of NPTX2 (n.d.). Retrieved from
https://www.proteinatlas.org./ENSG00000106236-NPTX2/tissue
Xiao, M.F., Xu, D., Craig, M.T., Pelkey, K.A., Chien, C.C., Shi, Y.,…Worley, P.F. (2017). NPTX2 and cognitive dysfunction in Alzheimer's disease. eLife, 6, e23798. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.23798
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Some journals stipulate that submitted articles cannot be under consideration for publication or published in another journal. The student-author and mentor have the option of determining which journal the paper will be submitted to first. UF JUR accepts papers that have been published in other journals or might be published in the future. It is the responsibility of the student-author and mentor to determine whether another journal will accept a paper that has been published in UF JUR.